A Dress Of White Silk Richard Matheson Pdf Printer
I can't install php7.0-mbstring: The following packages have unmet dependencies: php7.0-mbstring: Depends: php7.0-common (= 7.0.19-1) but 7.0.20-1~dotdeb+8.2 is to be installed E: Unable to correct problems, you have held broken packages. 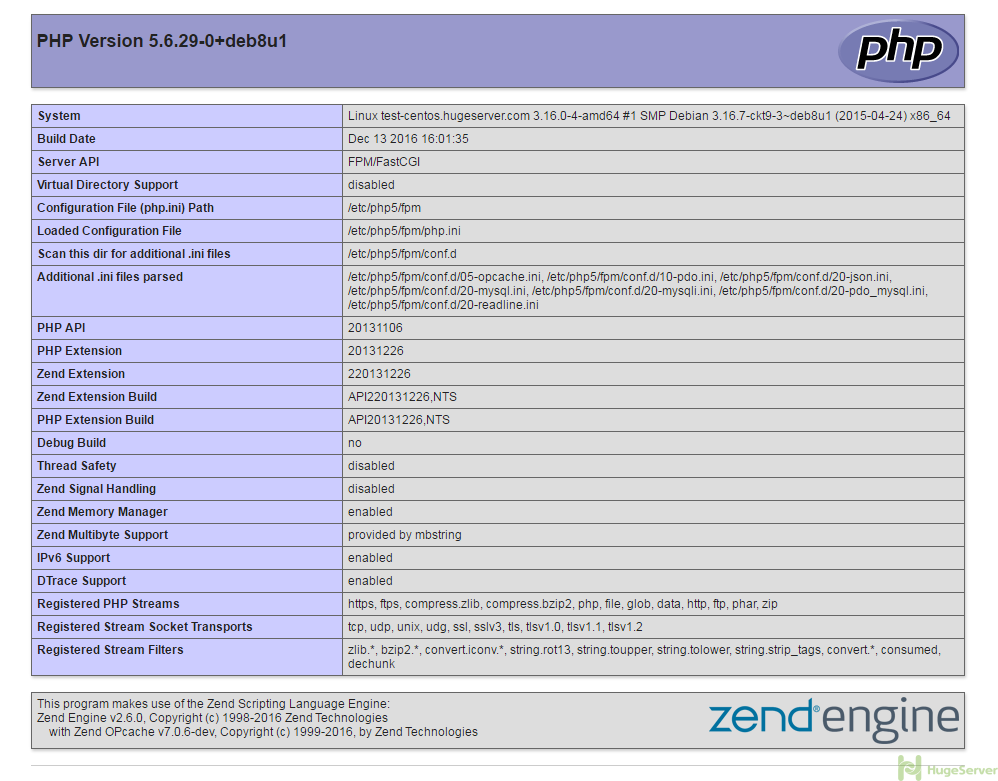
- Dress Of White Silk
- Dress Of White Silk Synopsis
- Dress Of White Silk Matheson
- Richard Matheson Dress Of White Silk
- A Dress Of White Silk Richard Matheson Pdf Printers
- A Dress Of White Silk Short Story
20 discussion posts. Martha said: I love Matheson's stories and I have read Dress of White Silk many times, but it seems a bit ambiguous as to its meanin.
- The Verve's Richard Ashcroft announces a solo tour. By Natalie Kuchik AXS Contributor Dec 12, 2016. The genre of news as we know it today is closely associated with the newspaper, which originated in China as a court bulletin and spread, with paper and printing press, to Europe.
- [Reading Room] Dress of White Silk by Richard Matheson I can see why so many episodes of the Twilight Zone start with the words “From a story by Richard Matheson.
To me, I see it as a little girl inheriting her mother's (evil?) power. Her mother may have been a witch? The ending also seems to imply that whatever 'terrible bad' thing she did, she gained some manner of power from.
Or, it could also mean the dress contains some leftover power of her mother's that possessed her while she held it.
Btw, this story has been reprinted many times, but here are two newer editions that contain it.
*SPOILERS*
As to what's going on - well, it's ambiguous on purpose, not just for the pay-off but also to forestall questions that might arise if too many details are given. Obviously the 'little girl' is normal enough to have a friend that visits, so she's no obvious monster, but that the mother herself probably appeared somewhat monstrous at her death (buck teeth = fangs, funny hands = claws), her shroud is the 'dress of white silk' and donning it either causes the daughter to be possessed by the mother or perhaps come into her inheritance of monstrous desire and power (the story hints that it has happened before). I actually think it's pretty evocative as is, asking questions just pulls an effective but flimsy structure apart.

Why does the grandmother allow a kid to come and play with the girl? Surely she knows something is not right because she screamed 'god help us its happened.'
Stuff just flies over my head sometimes in short stories. I didn't pick up on the buck teeth (fangs) or hands (claws) as being something other than the little girl worshiping her mother and not wanting to hear anything but how beautiful SHE thought her mother was. No wonder it was so dark in the house.
How'd I ever get my English degree?
Dress Of White Silk
'No she said she was so mad and red it has a hole in it.'
Although without punctuation, it seems to be it's saying that Mary Jane is mad and red and said, 'No, it has a hole in it.'
Tressa wrote: 'I also wonder about the hole in the 'red' dress. Maybe someone slammed a stake into it.'
The ending gives it away for me:
'She doesn't have to even give me supper. I'm not hungry anyway.
I'm full.'
The way Matherson emphasized that ending in his wording, tells me she ate Mary Jane.
'buck teeth funny hands' could be a werewolf or a vampire.
It seems obvious to me that the mother turns into a monster, and the child has inherited her tendency. For me, the big question is the role of the white dress. Here's a line that I'm puzzling the meaning of, when the daughter pretends to be the mother going out against the grandmother's wish:
'And oh stop your sobbing mother they will not catch me I have my magic dress.'
I searched through the story, and I still can't figure out how the dress is going to stop her from being captured. If she goes out and turns into a monster to claim her victims, what is the role of the dress?
It could be what you say, Shawn. Some clues that the dress has evil power:
The beginning where the girl was locked in her room:
'Because its happened she says. I guess I was bad. Only it was the dress.'
Later in the scene, she talked about her grandma:
'And she says I should burn it up but I loved her so. And she cries about the dress.'
After Mary Jane insulted her mother:
'I think the dress moved in my arms.'
'I think I heard some one call dont let her say that! I couldnt hold to the dress. And I had it on me I cant remember. Because I was grown up strong. But I was a little girl still I think I mean outside.
I think I was terrible bad then.'
My take on the dress:
1. The dress is a part of the mother, her monster, evil side. To destroy the dress is to destroy the mother. That's why the grandmother cannot destroy the dress.
2. Evil is passed on from the mother to the daughter, like the old concept, 'Sins of the father..', particularly mentioned here and there in the Bible.
I think the dress represents the evil that is within all of us and is also our inheritance.
In the Matheson's story terms, the dress transforms the mother into a supernaturally strong evil monster, so that man would have a hard time destroying her. Thus, she cannot be caught. Since that evil is an addictive part of her, she needs to don it every night to go out and commit her destruction.
I figured out the symbology of the dress of white silk while I was in the best thinking place, the shower. What dress of white silk is traditionally passed down from mother to daughter? A wedding dress! It represents an inheritance, and it represents a marriage. In this case, it is a marriage to the evil side. This is meant to be a story about innocence whose unavoidable inheritance is to be irrevocably married to the evil side upon maturity.
I figured out the symbology of the dress of white silk while I was in the best thinking place, the shower. What dress of white silk is traditionally passed down from mother to daug..'
Huh. I never thought of that at all. Interesting idea.
Dress Of White Silk Synopsis
back to topBooks mentioned in this topic
Nightmare At 20,000 Feet (other topics)Collected Stories, Vol. 1 (other topics)
I Am Legend and Other Stories (other topics)
Matheson in 2008 | |
| Born | Richard Burton Matheson February 20, 1926 Allendale, New Jersey, U.S. |
|---|---|
| Died | June 23, 2013 (aged 87) Los Angeles, California, U.S. |
| Pen name | Logan Swanson[1] |
| Occupation | Novelist, short story writer, screenwriter |
| Alma mater | University of Missouri |
| Period | 1950–2013 |
| Genre | Science fiction, fantasy, horror |
| Notable works | |
| Notable awards | World Fantasy Award for Life Achievement, Bram Stoker Award for Lifetime Achievement, Science Fiction Hall of Fame (2010) |
| Spouse | |
| Children | 4 |
| Signature | |
Richard Burton Matheson (February 20, 1926 – June 23, 2013) was an American author and screenwriter, primarily in the fantasy, horror, and science fiction genres. He is best known as the author of I Am Legend, a 1954 science fiction horror vampire novel that has been adapted for the screen four times, as well as the film Somewhere In Time for which he wrote the screenplay based on his novel Bid Time Return. Matheson also wrote 16 television episodes of The Twilight Zone, including 'Nightmare at 20,000 Feet' and 'Steel'. He adapted his 1971 short story 'Duel' as a screenplay directed by Steven Spielberg for the television film Duel that year. Seven of his novels and short stories have been adapted as motion pictures: The Shrinking Man, Hell House, What Dreams May Come, Bid Time Return (filmed as Somewhere in Time), A Stir of Echoes, Steel (filmed as Real Steel), and Button, Button (filmed as The Box). The movie Cold Sweat was based on his novel Riding the Nightmare, and Les seins de glace (Icy Breasts) was based on his novel Someone is Bleeding.
- 2Career
- 5Influence
- 6Works
Early life[edit]
Matheson was born in Allendale, New Jersey to Norwegian immigrants Bertolf and Fanny Matheson. They divorced when he was 8, and he was raised in Brooklyn, New York by his mother. His early writing influences were the film Dracula, novels by Kenneth Roberts, and a poem which he read in the newspaper Brooklyn Eagle,[2] where he published his first short story at age 8.[3] He entered Brooklyn Technical High School in 1939, graduated in 1943, and served with the Army in Europe during World War II; this formed the basis for his 1960 novel The Beardless Warriors.[2][4] He attended the Missouri School of Journalism at the University of Missouri, earning his BA in 1949, then moved to California.[2][3]
Career[edit]
1950s and 1960s[edit]
His first-written novel, Hunger and Thirst, was ignored by publishers for several decades before eventually being published in 2010, but his short story 'Born of Man and Woman' was published in The Magazine of Fantasy & Science Fiction, Summer 1950, the new quarterly's third issue[1] and attracted attention.[3] It is the tale of a monstrous child chained by its parents in the cellar, cast as the creature's diary in poignantly non-idiomatic English. Later that year he placed stories in the first and third numbers of Galaxy Science Fiction, a new monthly.[1] His first anthology of work was published in 1954.[3] Between 1950 and 1971, he produced dozens of stories, frequently blending elements of the science fiction, horror, and fantasy genres.
Reset Epson PX700W printer by WIC Utility tool is very simple. You can reset your Epson PX700W printer by Yourself + Watch video how to reset your Epson PX700W printer with WicReset Tools here. 
He was a member of the Southern California Sorcerers in the 1950s and 1960s, which included Charles Beaumont, Ray Bradbury, George Clayton Johnson, William F. Nolan, Jerry Sohl, and others.[5]
Several of his stories, including 'Third from the Sun' (1950), 'Deadline' (1959), and 'Button, Button' (1970) are simple sketches with twist endings; others, like 'Trespass' (1953), 'Being' (1954), and 'Mute' (1962) explore their characters' dilemmas over 20 or 30 pages. Some tales, such as 'The Doll that Does Everything' (1954) and 'The Funeral' (1955) incorporate satirical humour at the expense of genre clichés, and are written in an overblown prose very different from Matheson's usual pared-down style. Others, like 'The Test' (1954) and 'Steel' (1956), portray the moral and physical struggles of ordinary people, rather than the then nearly ubiquitous scientists and superheroes, in situations which are at once futuristic and everyday. Still others, such as 'Mad House' (1953), 'The Curious Child' (1954), and perhaps most of all, 'Duel' (1971), are tales of paranoia, in which the everyday environment of the present day becomes inexplicably alien or threatening. 'Duel' was adapted into the 1971 TV movie of the same name.
Matheson's first novel to be published, Someone Is Bleeding, appeared from Lion Books in 1953.[1] In 1960, Matheson published The Beardless Warriors, a non-fantastic, autobiographical novel about teenage American soldiers in World War II. It was filmed in 1967 as The Young Warriors though most of Matheson's plot was jettisoned. During the 1950s he published a handful of Western stories (later collected in By the Gun); and during the 1990s he published Western novels such as Journal of the Gun Years, The Gunfight, The Memoirs of Wild Bill Hickok, and Shadow on the Sun.
His other early novels include The Shrinking Man (1956, filmed in 1957 as The Incredible Shrinking Man, again from Matheson's own screenplay) and a science fiction vampire novel, I Am Legend (1954) (filmed as The Last Man on Earth in 1964, The Omega Man in 1971, and I Am Legend in 2007).
Matheson wrote screenplays for several television programs including the WesternsCheyenne, Have Gun – Will Travel, and Lawman.[6] He is most closely associated with the American TV series The Twilight Zone, for which he wrote more than a dozen episodes,[6] including 'Steel' (1963), 'Nightmare at 20,000 Feet' (1963), 'Little Girl Lost' (1962), and 'Death Ship' (1963). For all of his Twilight Zone scripts, Matheson wrote the introductory and closing statements spoken by creator Rod Serling.[7] He adapted five works of Edgar Allan Poe for Roger Corman's Poe series, including House of Usher (1960), The Pit and the Pendulum (1961), and The Raven (1963).[3]
He wrote the Star Trek episode 'The Enemy Within' (1966).
For Hammer Film Productions he wrote the screenplay for Fanatic (1965; US title: Die! Die! My Darling!) based on the novel Nightmare by Anne Blaisdell, starring Tallulah Bankhead and Stefanie Powers; he also adapted for Hammer Dennis Wheatley's The Devil Rides Out (1968).[3]
1970s and 1980s[edit]
In 1973, Matheson earned an Edgar Award from the Mystery Writers of America for his teleplay for The Night Stalker, one of two TV movies written by Matheson and directed by Dan Curtis (the other was The Night Strangler, which preceded the TV series Kolchak: The Night Stalker). Matheson worked extensively with Curtis; the 1977 television movie Dead of Night features three stories written for the screen by Matheson — 'Second Chance' (based on the story by Jack Finney); 'No Such Thing as a Vampire' (based on Matheson's story of the same name); and 'Bobby', an original script written for this omnibus movie by Matheson. 'Bobby' was later refilmed with different actors as the second segment of Trilogy of Terror II.
Three of his short stories were filmed together as Trilogy of Terror (1975), including 'Prey' (initially published in the April 1969 issue of Playboy magazine) with its famous Zuni warrior fetish doll. The Zuni fetish doll reappeared in the final segment of the belated sequel to the first movie, Trilogy of Terror II.
Other Matheson novels turned into notable films in the seventies include Bid Time Return (as Somewhere in Time), and Hell House (as The Legend of Hell House), both adapted and scripted by Matheson himself.
In the 1980s, Matheson published the novel Earthbound, wrote several screenplays for the TV series Amazing Stories, and continued to publish short fiction.
1990s[edit]
Matheson published four western novels in this decade, plus the suspense novel Seven Steps to Midnight (1993) and the blackly comic locked-room mystery novel, Now You See It .., aptly dedicated to Robert Bloch (1995).
He also wrote several movies—the offbeat comedy and box-office flop Loose Cannons, the biopic The Dreamer of Oz (about L. Frank Baum), a segment of Rod Serling's Lost Classics, and segments of Trilogy of Terror II. Short stories continued to flow from his pen, and he saw the adaptations by other hands of two more of his novels for the big screen—What Dreams May Come and A Stir of Echoes (as Stir of Echoes). In 1999, Matheson published a non-fiction work The Path, inspired by his interest in psychic phenomena.[3]
21st century[edit]
Many previously unpublished novels by Matheson appeared late in his career, as did various collections of his work and previously unpublished screenplays. He also wrote new works, such as the suspense novel Hunted Past Reason (2002).[8] and the children's illustrated fantasy Abu and the Seven Marvels.
Sources of inspiration[edit]
Matheson cited specific inspirations for many of his works. Duel was derived from an incident in which he and a friend, Jerry Sohl, were dangerously tailgated by a large truck on the same day as the assassination of John F. Kennedy.[3]
According to film criticRoger Ebert, Matheson's scientific approach to the supernatural in I Am Legend and other novels from the 1950s and early 1960s 'anticipated pseudorealistic fantasy novels like Rosemary's Baby and The Exorcist.'[9]
Personal life and death[edit]
In 1952, Matheson married Ruth Ann Woodson, whom he met in California. They had four children.[2] Bettina Mayberry, Richard Christian Matheson, Chris Matheson and Ali Matheson.
Richard Christian, Chris and Ali became writers of fiction and screenplays.

Matheson died on June 23, 2013 at his home in Los Angeles, California, at the age of 87.[10][11][12]
Awards[edit]
Matheson received the World Fantasy Award for Life Achievement in 1984 and the Bram Stoker Award for Lifetime Achievement from the Horror Writers Association in 1991. The Science Fiction Hall of Fame inducted him in 2010.[13][14]
At the annual World Fantasy Conventions he won two judged, annual literary awards for particular works: World Fantasy Awards for Bid Time Return as the best novel of 1975 and Richard Matheson: Collected Stories as the best collection of 1989.[13][15]
Matheson died just days before he was due to receive the Visionary award at the 39th Saturn Awards ceremony. As a tribute, the ceremony was dedicated to him and the award was presented posthumously. Academy President Robert Holguin said 'Richard's accomplishments will live on forever in the imaginations of everyone who read or saw his inspired and inimitable work.'[16][failed verification]
The tribute anthology He is Legend was published by Gauntlet Press in 2009.
Influence[edit]
Other writers[edit]
Stephen King has listed Matheson as a creative influence and his novel Cell is dedicated to Matheson, along with filmmaker George A. Romero. Romero frequently acknowledged Matheson as an inspiration and listed the shambling vampire creatures that appear in The Last Man on Earth, the first film version of I Am Legend, as the inspiration for the zombie 'ghouls' he envisioned in Night of the Living Dead[17]
Anne Rice stated that when she was a child, Matheson's short story 'A Dress of White Silk' was an early influence on her interest in vampires and fantasy fiction.[18][full citation needed]
Dress Of White Silk Matheson
Directors[edit]
After his death, several figures offered tributes to his life and work. Director Steven Spielberg said:
| “ | Richard Matheson's ironic and iconic imagination created seminal science-fiction stories and gave me my first break when he wrote the short story and screenplay for Duel. His Twilight Zones were among my favorites, and he recently worked with us on Real Steel. For me, he is in the same category as Bradbury and Asimov.[19] | ” |
Another frequent collaborator, Roger Corman said:
| “ | Richard Matheson was a close friend and the best screenwriter I ever worked with. I always shot his first draft. I will miss him.[20] | ” |
Richard Matheson Dress Of White Silk
On Twitter, director Edgar Wright wrote 'If it's true that the great Richard Matheson has passed away, 140 characters can't begin to cover what he has given the sci fi & horror genre.' Director Richard Kelly added 'I loved Richard Matheson's writing and it was a huge honor getting to adapt his story 'Button, Button' into a film. RIP.'[21]
Works[edit]
Novels[edit]
- Someone Is Bleeding (1953) filmed as Icy Breasts
- Fury on Sunday (1953)
- I Am Legend (1954) filmed as The Last Man on Earth, The Omega Man, I Am Omega and I Am Legend
- The Shrinking Man (1956); filmed as The Incredible Shrinking Man and subsequently reprinted under that title; also the basis of the film The Incredible Shrinking Woman
- A Stir of Echoes (1958); filmed as Stir of Echoes
- Ride the Nightmare (1959); adapted as an episode of The Alfred Hitchcock Hour and later filmed as Cold Sweat (1970 film)
- The Beardless Warriors (1960); filmed as The Young Warriors
- The Comedy of Terrors (1964), with Elsie Lee; filmed as The Comedy of Terrors
- Hell House (1971); filmed as The Legend of Hell House
- Bid Time Return (1975); filmed as Somewhere in Time and subsequently reprinted under that title
- What Dreams May Come (1978); filmed as What Dreams May Come
- Earthbound (Playboy Publications, 1982), as by Logan Swanson[1] – editorially abridged version; restored text published as by Richard Matheson, UK: Robinson Books, 1989
- Journal of the Gun Years (1992)
- The Gunfight (1993)
- 7 Steps to Midnight (1993)
- Shadow on the Sun (1994)
- Now You See It .. (1995)
- The Memoirs of Wild Bill Hickock (1996)
- Passion Play (2000)
- Hunger and Thirst (2000)
- Camp Pleasant (2001)
- Abu and the Seven Marvels (2002)
- Hunted Past Reason (2002)
- Come Fygures, Come Shadowes (2003)
- Woman (2006)
- Other Kingdoms (2011)
- Generations (2012)
Short stories[edit]
- 'Born of Man and Woman' (1950)
- 'Third from the Sun' (1950); adapted as a Twilight Zoneepisode (1960)
- 'The Waker Dreams' (a.k.a. 'When the Waker Sleeps') (1950)
- 'Blood Son' (1951)
- 'Through Channels' (1951)
- 'Clothes Make the Man' (1951)
- 'Return' (1951)
- 'The Thing' (1951)
- 'Witch War' (1951)
- 'Dress of White Silk' (1951)
- 'F---' (a.k.a. 'The Foodlegger') (1952)
- 'Shipshape Home' (1952)
- 'SRL Ad' (1952)
- 'Advance Notice' (a.k.a. 'Letter to the Editor') (1952)
- 'Lover, When You're Near Me' (1952)
- 'Brother to the Machine' (1952)
- 'To Fit the Crime' (1952)
- 'The Wedding' (1953)
- 'Wet Straw' (1953)
- 'Long Distance Call' (a.k.a. 'Sorry, Right Number') (1953)
- 'Slaughter House' (1953)
- 'Mad House' (1953)
- 'The Last Day' (1953)
- 'Lazarus II' (1953)
- 'Legion of Plotters' (1953)
- 'Death Ship' (1953); adapted as a Twilight Zoneepisode (1963)
- 'Disappearing Act' (1953); adapted as a Twilight Zoneepisode (1959)
- 'The Disinheritors' (1953)
- 'Dying Room Only' (1953)
- 'Full Circle' (1953)
- 'Mother by Protest' (a.k.a. 'Trespass') (1953)
- 'Little Girl Lost' (1953); adapted as a Twilight Zoneepisode (1962)
- 'Being' (1954)
- 'The Curious Child' (1954)
- 'When Day Is Dun' (1954)
- 'Dance of the Dead' (1954); adapted as a Masters of Horrorepisode (2005)
- 'The Man Who Made the World' (1954)
- 'The Traveller' (1954)
- 'The Test' (1954)
- 'The Conqueror' (1954)
- 'Dear Diary' (1954)
- 'The Doll That Does Everything' (1954)
- 'Descent' (1954)
- 'Miss Stardust' (1955)
- 'The Funeral' (1955); adapted as story segment for Rod Serling's Night Gallery
- 'Too Proud to Lose' (1955)
- 'One for the Books' (1955)
- 'Pattern for Survival' (1955)
- 'A Flourish of Strumpets' (1956)
- 'The Splendid Source' (1956); the basis of the Family Guy episode 'The Splendid Source'.[22]
- 'Steel' (1956); adapted as a Twilight Zoneepisode (1963); loosely filmed as Real Steel (2011)
- 'The Children of Noah' (1957)
- 'A Visit to Santa Claus' (a.k.a. 'I'll Make It Look Good,' as Logan Swanson) (1957)
- 'The Holiday Man' (1957)
- 'Old Haunts' (1957)
- 'The Distributor' (1958)
- 'The Edge' (1958)
- 'Lemmings' (1958)
- 'Now Die in It' (1958)
- 'Mantage' (1959)
- 'Deadline' (1959)
- 'The Creeping Terror' (a.k.a. 'A Touch of Grapefruit') (1959)
- 'No Such Thing as a Vampire' (1959); adapted as segment of the TV film Dead of Night (1977 film)
- 'Big Surprise' (a.k.a. 'What Was in the Box') (1959) Adapted as a Night Gallery short
- 'Crickets' (1960)
- 'Day of Reckoning' (a.k.a. 'The Faces,' 'Graveyard Shift') (1960)
- 'First Anniversary' (1960); adapted as an Outer Limitsepisode (1996)
- 'From Shadowed Places' (1960)
- 'Nightmare at 20,000 Feet' (1961); adapted as The Twilight Zoneepisode in 1963 and as segment four of Twilight Zone: The Movie in 1983
- 'Finger Prints' (1962)
- 'Mute' (1962); adapted as a Twilight Zoneepisode (1963)
- 'The Likeness of Julie' (as Logan Swanson) (1962); adapted into 'Julie' in the 1975 TV film Trilogy of Terror
- 'The Jazz Machine' (1963)
- 'Crescendo' (a.k.a. 'Shock Wave') (1963)
- 'Girl of My Dreams' (1963); adapted by Robert Bloch and Michael J. Bird as an episode of the 1968 Hammer TV series Journey to the Unknown
- 'Tis the Season to Be Jelly' (1963)
- 'Deus Ex Machina' (1963)
- 'Interest' (1965)
- 'A Drink of Water' (1967)
- 'Needle in the Heart' (a.k.a. 'Therese') (1969); adapted into 'Millicent and Therese' in the 1975 TV film Trilogy of Terror
- 'Prey' (1969); adapted into 'Ameilia' in the 1975 TV film Trilogy of Terror
- 'Button, Button' (1970); filmed as a The Twilight Zoneepisode in 1986; filmed as The Box (2009)
- 'Til Death Do Us Part' (1970)
- 'By Appointment Only' (1970)
- 'The Finishing Touches' (1970)
- 'Duel' (1971); filmed as Duel (1971)
- 'Big Surprise' (1971); adapted as story segment for Rod Serling's Night Gallery
- 'Leo Rising' (1972)
- 'Where There's a Will' (with Richard Christian Matheson) (1980)
- 'And Now I'm Waiting' (1983)
- 'Blunder Buss' (1984)
- 'Getting Together' (1986)
- 'Buried Talents' (1987)
- 'The Near Departed' (1987)
- 'Shoo Fly' (1988)
- 'Person to Person' (1989)
- 'CU: Mannix' (1991)
- 'Two O'Clock Session' (1991)
- 'The Doll' (as Amazing Stories in 1986)
- 'Go West, Young Man' (1993)
- 'Gunsight' (1993)
- 'Little Jack Cornered' (1993)
- 'Of Death and Thirty Minutes' (1993)
- 'Always Before Your Voice' (1999)
- 'Relics' (1999)
- 'And in Sorrow' (2000)
- 'The Prisoner' (2001)
- 'Purge Among Peanuts' (2001)
- 'He Wanted to Live' (2002)
- 'The Last Blah in the Etc.' (a.k.a. 'All and Only Silence') (2002)
- 'Life Size' (2002)
- 'Maybe You Remember Him' (2002)
- 'Mirror, Mirror..' (2002)
- 'Phone Call From Across The Street' (2002)
- 'Professor Fritz and the Runaway House' (2002)
- 'That Was Yesterday' (2002)
- 'Man With a Club' (2003)
- 'Haircut' (2006)
- 'Life Size' (2008)
- 'An Element Never Forgets' (2010)
- 'Backteria' (2011)
A Dress Of White Silk Richard Matheson Pdf Printers
Short story collections[edit]
- Born of Man and Woman (1954)
- The Shores of Space (1957)
- Shock! (1961)
- Shock 2 (1964)
- Shock 3 (1966)
- Shock Waves (1970) Published as Shock 4 in the UK (1980)
- Button, Button (1970) basis for the movie, 'The Box' (2009)
- Richard Matheson: Collected Stories (1989)
- By the Gun (1993)
- Nightmare at 20,000 Feet (2000)
- Pride with Richard Christian Matheson (2002)
- Duel (2002)
- Offbeat: Uncollected Stories (2002)
- Darker Places (2004)
- Unrealized Dreams (2004)
- Duel and The Distributor (2005) Previously unpublished screenplays of these two stories
- Button, Button: Uncanny Stories (2008) (Tor Books)
- Uncollected Matheson: Volume 1 (2008)
- Uncollected Matheson: Volume 2 (2010)
- Steel: And Other Stories (2011)
- Bakteria and Other Improbable Tales (2011) (e-book exclusive)
- The Best of Richard Matheson (2017) (Penguin Classics)
Films (for TV movies see Television below)[edit]
A Dress Of White Silk Short Story
- The Incredible Shrinking Man (1957)
- The Beat Generation (1959)
- House of Usher (1960)
- Master of the World (1961)
- The Pit and the Pendulum (1961)
- Burn Witch Burn (1962); a.k.a. Night of the Eagle (screenplay co-written with Charles Beaumont and George Baxt) based on the novel Conjure Wife by Fritz Leiber
- Tales of Terror (1962)
- The Raven (1963)
- The Comedy of Terrors (1963)
- The Last Man on Earth (as 'Logan Swanson', based on Matheson's novel I Am Legend) (1964)
- Fanatic (1965)
- The Young Warriors (based on Matheson's novel The Beardless Warriors) (1967)
- The Devil Rides Out (based on the novel by Dennis Wheatley) (1968)
- De Sade (1969)
- Cold Sweat (based on Matheson's novel Ride the Nightmare) (1970)
- The Omega Man (based on Matheson's novel I Am Legend) (1971)
- The Legend of Hell House (based on Matheson's novel Hell House) (1973)
- Icy Breasts (based on his novel Someone Is Bleeding) (1974)
- Somewhere in Time (based on his novel Bid Time Return) (1980)
- Twilight Zone: The Movie: Fourth segment 'Nightmare at 20,000 Feet' (1983)
- Jaws 3-D (1983)
- Loose Cannons (1990)
- What Dreams May Come (based on Matheson's novel) (1998)
- Stir of Echoes (1999)
- I Am Legend (based on Matheson's novel) (2007)
- The Box (2009)
- Real Steel (2011)
Television[edit]
- Buckskin: 'Act of Faith' (1959)
- Wanted Dead or Alive :'The Healing Woman' (1959)
- Twilight Zone: (16 episodes) (1959–1964)
- Have Gun Will Travel: 'The Lady on The Wall' (1960)
- Bourbon Street Beat: 'Target of Hate' (1960)
- Cheyenne: 'Home Is The Brave' (1960)
- Lawman (Six episodes) (1960–1962)
- Thriller: 'The Return of Andrew Bentley' (1961)
- Combat!: 'Forgotten Front' (as Logan Swanson) (1962)
- The Alfred Hitchcock Hour: 'Ride the Nightmare' (1962)
- The Alfred Hitchcock Hour: 'The Thirty-First of February' (1963)
- The Girl from U.N.C.L.E.: 'The Atlantis Affair' (1966)
- Bob Hope Presents The Chrysler Theater : 'Time of Flight' (1966)
- Star Trek: The Original Series: 'The Enemy Within' (1966)
- Duel (1971)
- The Night Stalker (1972)
- Night Gallery (1972): ' The Funeral' (1972)
- The Night Strangler (1973)
- Dying Room Only (1973)
- Circle of Fear (originally titled Ghost Story (1973))
- Bram Stoker's Dracula (1974)
- Scream of the Wolf (1974)
- The Morning After (1974)
- Trilogy of Terror (1975) TV omnibus movie directed by Dan Curtis.
- Dead of Night (1977). TV omnibus movie directed by Dan Curtis.
- The Strange Possession of Mrs. Oliver (1977)
- The Martian Chronicles mini-series (1979, 1980)
- Twilight Zone: 'Button, Button' (as Logan Swanson) (1986)
- Amazing Stories: 'The Doll' (1986)
- Amazing Stories: 'One for the Books' (1987)
- Dreamer of Oz (1990). About L. Frank Baum.
- Rod Serling's Lost Classics (1994)
- Trilogy of Terror II (1996) TV omnibus movie directed by Dan Curtis.
Nonfiction[edit]
- The Path: Metaphysics for the 90s (1993)
- The Path: A New Look at Reality (1999)
Further reading[edit]
- California Sorcery, edited by William F. Nolan and William Schafer
- Jad Hatem, Charité de l'infinitésimal, Paris, L'Harmattan, 2007
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ abcdeRichard Matheson at the Internet Speculative Fiction Database (ISFDB). Retrieved April 13, 2013. Select a title to see its linked publication history and general information. Select a particular edition (title) for more data at that level, such as a front cover image or linked contents.
- ^ abcd'Richard Matheson Biography: Author, Screenwriter (1926–2013)'. Biography.com (FYI and A&E Networks). Archived from the original on September 13, 2015. Retrieved September 29, 2015.Cite uses deprecated parameter
deadurl=(help) - ^ abcdefghHawtree, Christopher (June 25, 2013). 'Richard Matheson obituary'. Guardian.co.uk. London. Retrieved June 26, 2013.
- ^Sammon, Paul M. (October 1979). 'Richard Matheson: Master of Fantasy'. Fangoria (2): 26–29, 52 – via Internet Archive.
- ^Conlon, Christopher 'Southern California Sorcerers', [1], October 1999. Retrieved October 31, 2012.
- ^ abWeber, Bruce (June 25, 2013). 'Richard matheson, Writer of Haunted Science Fictionand Horror, Dies at 87'. New York Times. Retrieved June 26, 2013.
- ^Alexander, Chris (March 2011). 'The Legend of Richard Matheson'. Fangoria. New York City: The Brooklyn Company, Inc. (301): 47.
.. the things Serling said at the beginning and the end, in the wraparounds, which I wrote. I wrote all the wraparounds to my Twilight Zone episodes.
- ^What Screams May Come: A Look at the Legendary Richard Matheson.[full citation needed]
- ^Ebert, Roger (1989). Roger Ebert's Movie Home Companion (1990 ed.). Andrews and McMeel. p. 419. ISBN978-0836262407.
- ^'Richard Matheson (1926–2013'. Locus Publications. June 24, 2013. Retrieved June 25, 2013.
- ^Kellogg, Carolyn (June 24, 2013). ''I Am Legend' Author Richard Matheson Has Died at 87'. Los Angeles Times. Retrieved June 24, 2013.
- ^'Richard Matheson: Sci-Fi Author Dies Aged 87'. Sky News. June 25, 2013. Retrieved June 25, 2013.
- ^ ab'Matheson, Richard'. The Locus Index to SF Awards: Index of Literary Nominees. Locus Publications. Retrieved April 13, 2013.
- ^'Science Fiction Hall of Fame'. Experience Music Project and Science Fiction Museum and Hall of Fame. Archived from the original on March 25, 2010.
EMP SFM is proud to announce the 2010 Hall of Fame inductees: ..
Cite uses deprecated parameterdeadurl=(help) - ^'Award Winners and Nominees'. World Fantasy Convention. Archived from the original on December 1, 2010. Retrieved February 4, 2011.Cite uses deprecated parameter
dead-url=(help) - ^'39th annual Saturn Awards to be dedicated to the memory of author Richard Matheson'. Hitfix.com. Retrieved June 26, 2013.
- ^Deborah Christie, Sarah Juliet Lauro, ed. (2011). Better Off Dead: The Evolution of the Zombie as Post-Human. Fordham Univ Press. p. 169. ISBN0-8232-3447-9, 9780823234479.
- ^Entertainment Weekly. August 7, 2009.Missing or empty
title=(help)[full citation needed] - ^'I am Legend writer Richard Matheson dies aged 87'. LondonEvening Standard. Retrieved June 26, 2013.
- ^Olsen, Mark (June 24, 2013). ''I Am Legend' writer Richard Matheson's legacy of smart sci-fi'. Los Angeles Times. Retrieved June 26, 2013.
- ^Tobin, Christian (June 24, 2013). 'Richard Matheson dies:Tributes paid to I am Legend, Twilight Zone Icon'. Digital Spy. Retrieved June 26, 2013.
- ^Steel: And Other Stories. Product Description.[full citation needed]
External links[edit]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Richard Matheson. |
| Wikiquote has quotations related to: Richard Matheson |
- Richard Matheson at the Internet Speculative Fiction Database
- Matheson biography at tabula-rasa.info
- Richard Matheson featured on AMC-TV's Sci-Fi Department webshow
- Richard Matheson on IMDb
- Richard Matheson at Memory Alpha (a Star Trekwiki)
- 'Richard Matheson biography'. Science Fiction and Fantasy Hall of Fame.